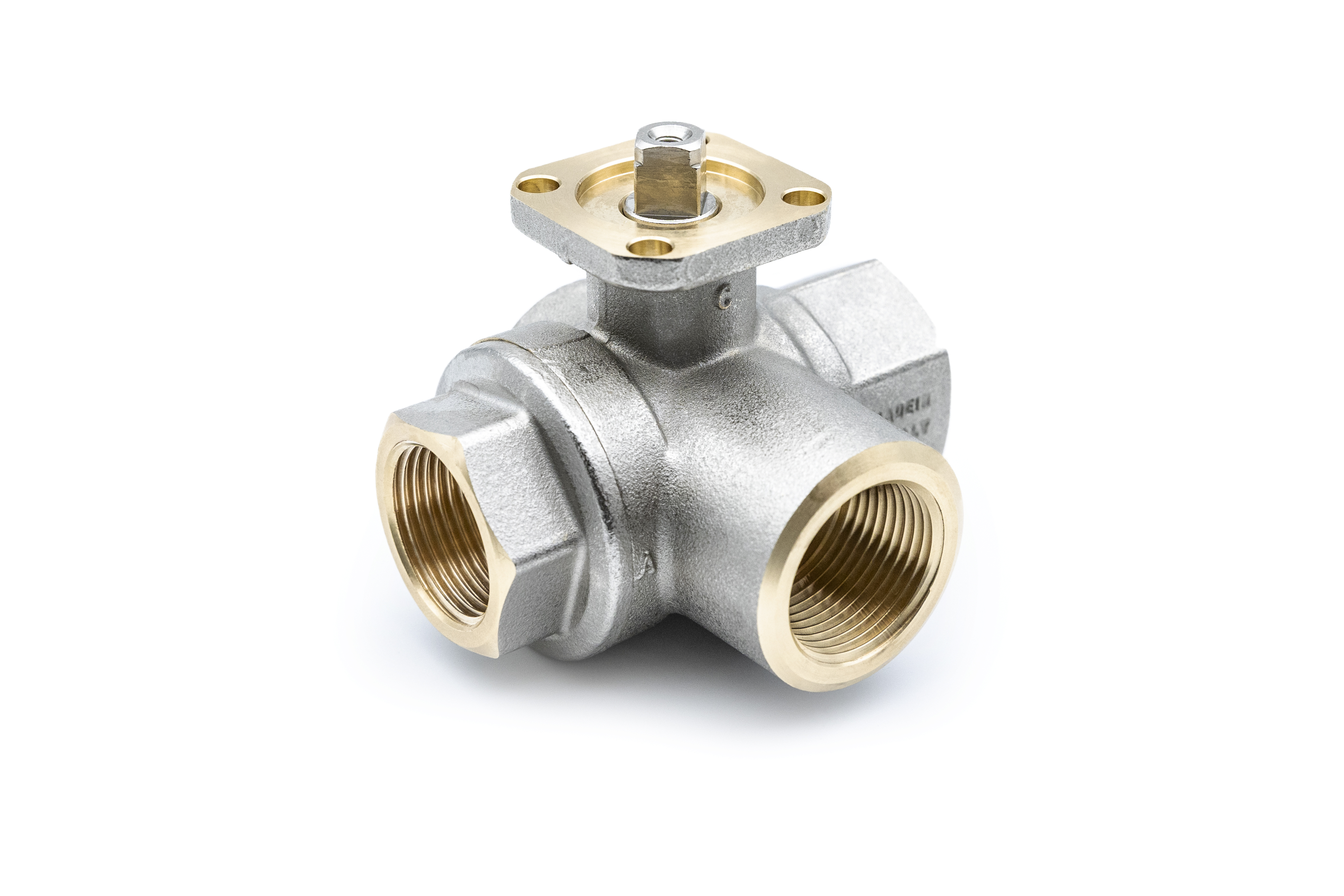
マルチポートバルブであるs.7350シリーズは、省コスト化、および省スペース化を図ります。本製品は、4面シートの採用により全て のポートにボールシートを採用しているため、適用範囲が大きく拡大。どのポートも、遮断可能。ボールポート構成の特定化、およ び独自のTポート設計によって、流れ方向を自由に選ぶことができます。従来は必要だった複数の流体搬送ラインの合理化・簡素化を実現し、設備全体のコスト削減にも、大きく貢献する万能バルブです。
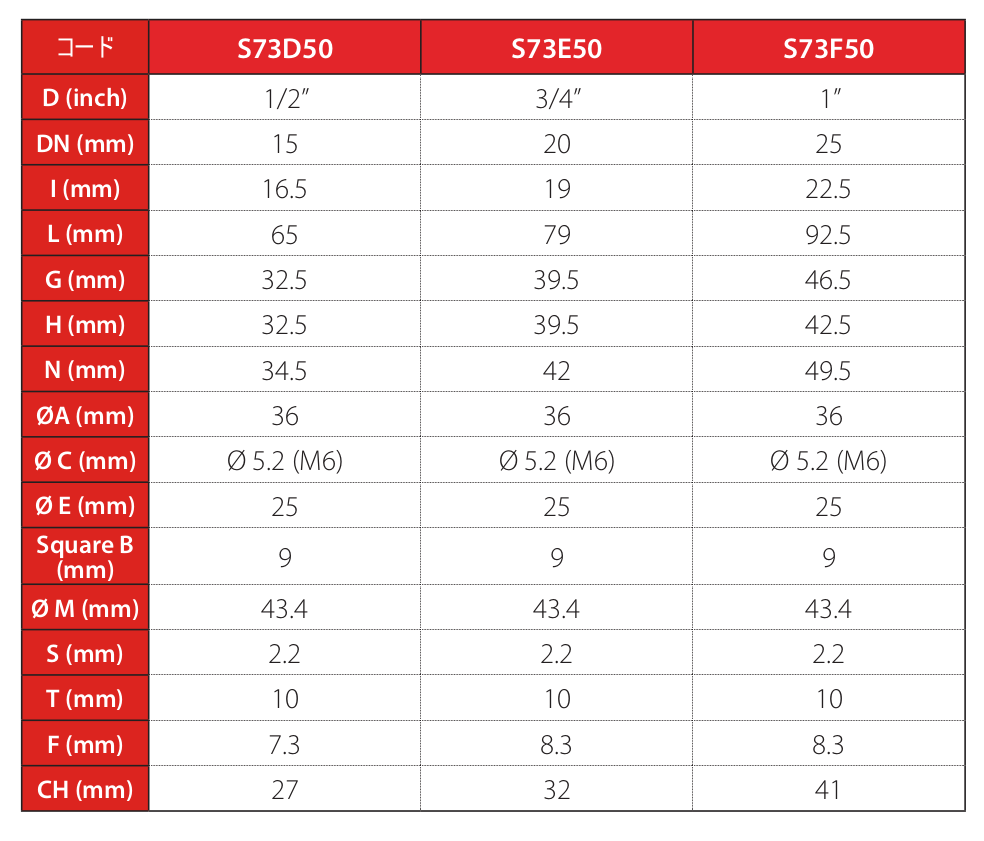
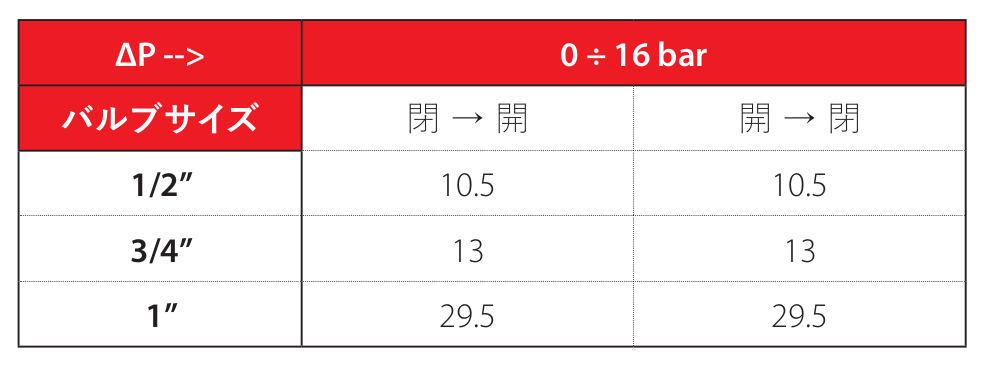
技術データ
- 100%シールテストを保証
- 金属間可動部なし
- メンテナンスフリー
- シリコンフリー潤滑剤使用
- クロームメッキされた真鍮ボールの高い耐久性
- どのボール方向でも、好パフォーマンスを発揮
- 剛健な作り
- 熱鍛造サンドブラスト処理を施した、外部ニッケルメッキボディ
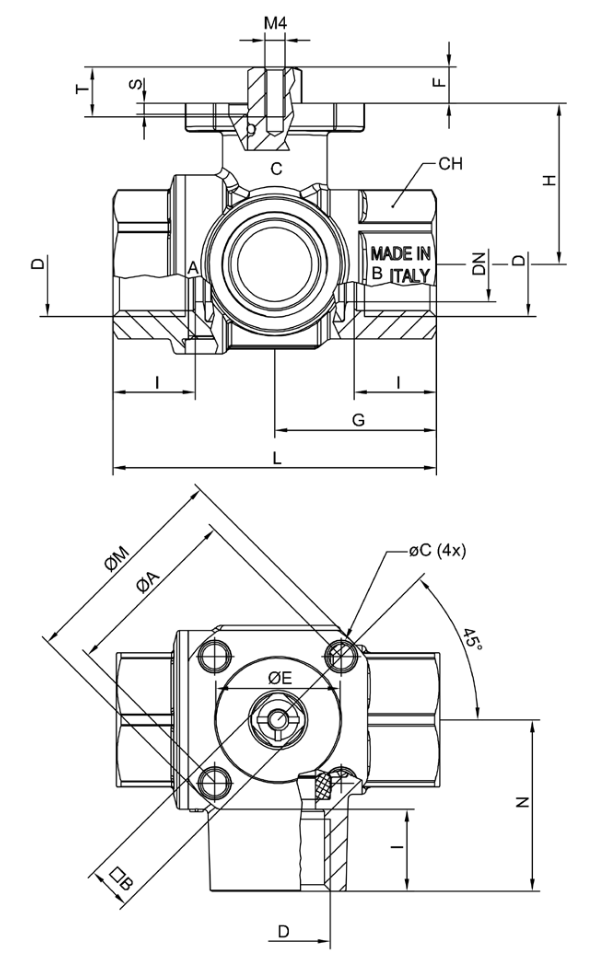
及びエンドキャップ - ISO 5211、および DIN 3337 に準ずるマウントフランジを採用
し、アクチュエータ接続向けのユニバーサルジョイントに対応 - EN12165及びEN12164に準拠する高品質の真鍮材を使用
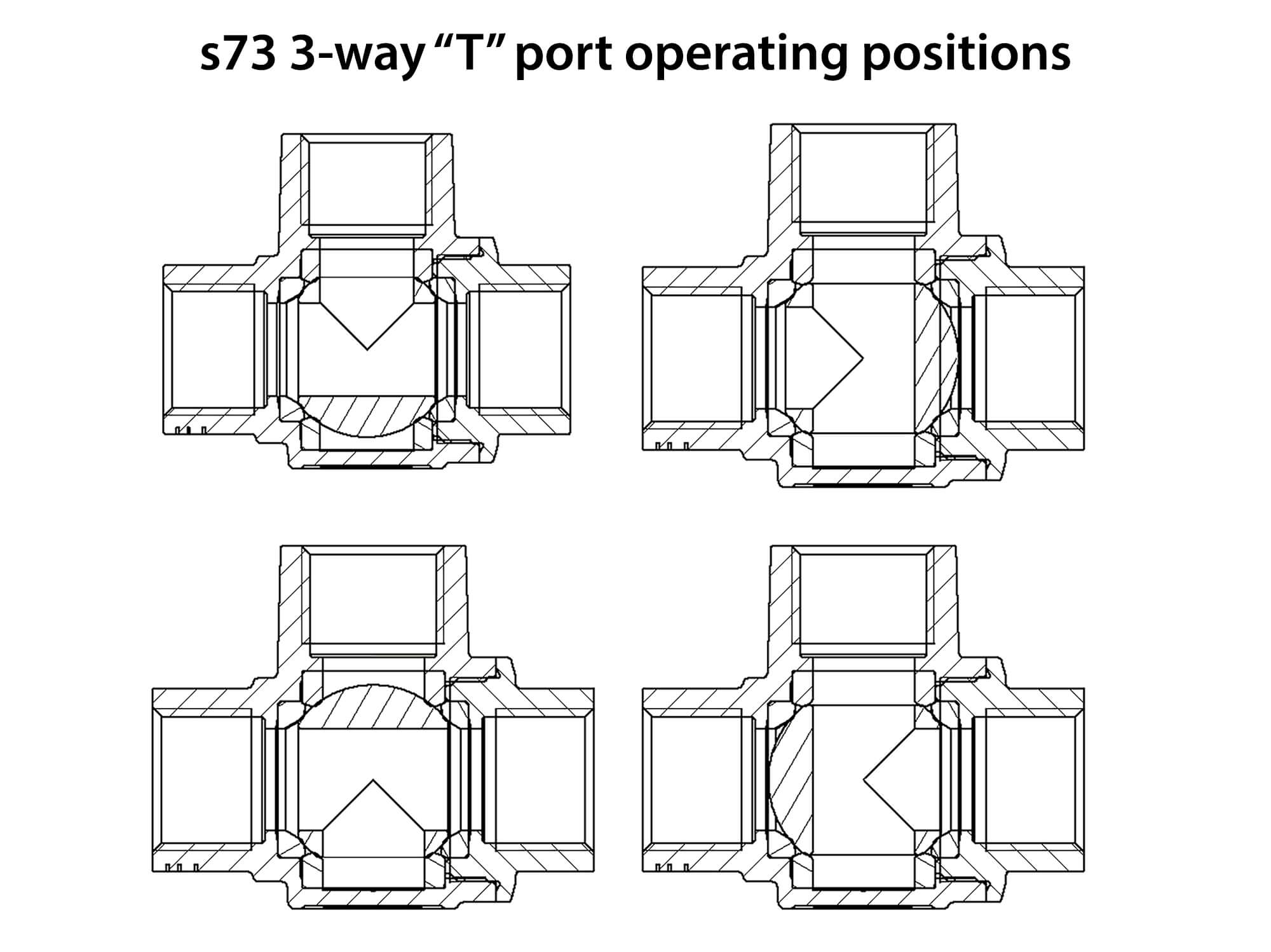
- 3-方向 T ポート 設計で、複数流路に対応
- 飛び出し防止設計ステムで安全確保
- 二枚のFPM製Oリングがステムの安全性を確保
- フレキシブルリップ設計の純PTFEシート
- 4ヵ所設計で、さまざまな流体に対応
- ISO 7/1、BS21 BSPT テーパーネジ仕様(JIS B 0203 相当)
- フルボア最大流量を確保
- ラック及びピニオン式 ニューマチッククアクチュエータ
(スプリングリターン式またはダブルアクティング式) - アクセサリーとして、またはすでに取り付けられているロッ
ク可能なハンドル - スクリュー付きアダプターフランジキット
- EN 10226-1、ISO 228 平行メス x メスネジ
- ANSI B.1.20.1 NPTメネジ構造
- カスタム設計
- ステンレス製ステム
- 2 シート L-ポート設計 (s.7650)
- 耐圧:2MPa (300 PSI)[常温・通常圧]
- 温度:-20℃ ~ +150℃
注意: 流体の凍結はバルブ本体の損傷に繋がる恐れがあります
- RoHS 準拠品
注意: 認証は特定の設計・サイズに適応されます
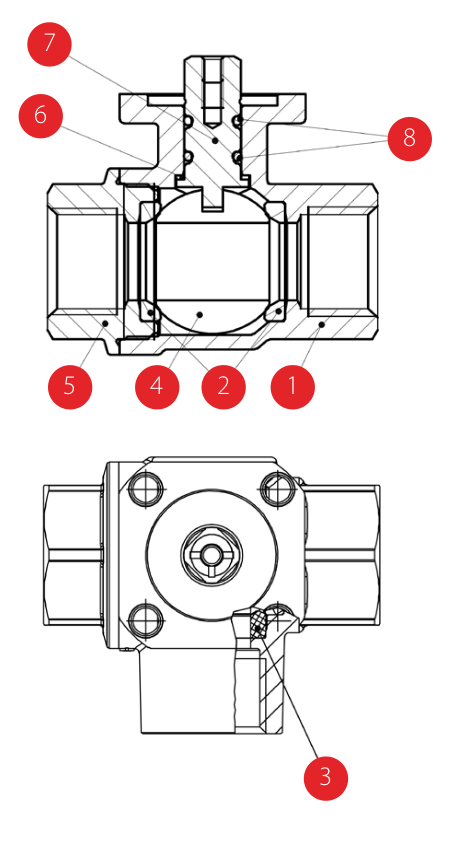
| 部品説明 | 個数 | 材質 |
|---|---|---|
|
ニッケルメッキボディ (外部ニッケルメッキ・内部ニッケル メッキ無し)
|
1
|
CW617N (C3771相当)
|
|
シート
|
2
|
PTFE
|
|
シート
|
2
|
PTFE
|
|
クロームメッキボール
|
1
|
CW617N (C3771相当)
|
|
ニッケルメッキエンドキャップ (外部ニッケルメッキ・内部ニッケル メッキ無し)
|
1
|
CW617N (C3771相当)
|
|
ワッシャー
|
1
|
PTFEカーボン充填25%
|
|
ニッケルメッキステムOリング設計
|
1
|
CW617N (C3771相当)
|
|
Oリング
|
2
|
FPM
|